In our previous blog, we discussed how AI agents will transform B2B sales. But what does this look like in practice? Let’s imagine a machinery company selling worldwide. Beyond physical products like spare parts, they also want to scale service sales for maintenance.
Bringing AI agents into a global manufacturing context
The machinery company operates in a complex environment with a global customer base, fluctuating demand, and high expectations for service reliability. Succeeding in this landscape requires real-time visibility into product availability, fast and dependable delivery scheduling, and the flexibility to develop new revenue streams through service-based models.
How could agentic AI make a difference in this setting? We see three likely scenarios.
Scenario 1 – What the hype promises
In the hype scenario, agents handle all global expansion including 24/7 orders from new markets, automated service contracts, and proactive part replacements based on maintenance plans. Revenue scales without matching headcount.
Scenario 2 – A siloed mess
Every department launches its own AI initiative without alignment. Agents clash, data is inconsistent, and customers get confusing or contradictory responses. Instead of efficiency, you get chaos. In addition, the realized value can often remain low and the solutions don’t scale.
Scenario 3 – Hybrid model (the realistic path)
This is the path we see as the most likely and the most impactful. Agents handle routine workflows such as reorders, ticket and customer service, and standard quoting, freeing people to focus on strategic accounts, relationship building, and governance. This balance keeps efficiency high while maintaining trust. In this scenario, human abilities are enhanced, and a person becomes the driver of a swarm of agents.
- Agents can automate heavily manual processes and change the way we buy, sell, and collaborate with merchants.
- The reality of reaching true personalization is closer than ever
- Humans are the guiding force of agentic operations, ensuring reliability
In a hybrid scenario, several groups within the company will interact and collaborate with AI agents. The primary users are the sales teams, digital sales teams, customer service, and marketing teams. Secondary users include procurement, finance, and compliance departments.
What to keep in mind when moving toward agentic commerce
There are several key things to keep in mind across all the scenarios outlined above:
Improving data quality for agentic use.
Using standard protocols to ensure security and reliability of agentic services.
Leveraging the agentic commerce protocol on existing sales channels.
Integrating agentic AI with current systems and processes.
Maintaining strong security and compliance.
Sharing information with agents while protecting competitive advantage.
Perhaps the most important opportunity lies in data. Each interaction depends on having the right information surfaced in the right context. AI can help improve data quality, but in most cases, there is work required to get the needed data in place.
A spare-parts agent, for example, relies on clean product hierarchies and compatibility data, while a pricing agent performs best when contract terms are clearly defined. In short, strong data leads to strong outcomes. However, this doesn’t have to turn into a massive five-year data governance program. We can start by experimenting with small data sets and use AI itself to detect patterns and improve data quality.
The primary benefits of agentic AI for business
We see there are three primary areas where agentic AI delivers a strong return on investment (ROI) in commerce:
1. Commercial data intelligence: In practice, this often means automatically managing product information and handling data enrichment more smoothly. This leads to faster time-to-market, lower enrichment costs, and fewer data errors.
2. Automatic operations: Examples include simplifying complex order processing and improving fulfillment. Automatic operations help reduce processing costs, boost efficiency, and cut down on errors in order workflows, leading to happier B2B and D2C customers.
3. Enhanced experience: AI is finally making possible the level of personalization we’ve talked about in digital commerce for two decades. Real personalization enables higher conversion rates, larger basket sizes, and faster deal cycles.
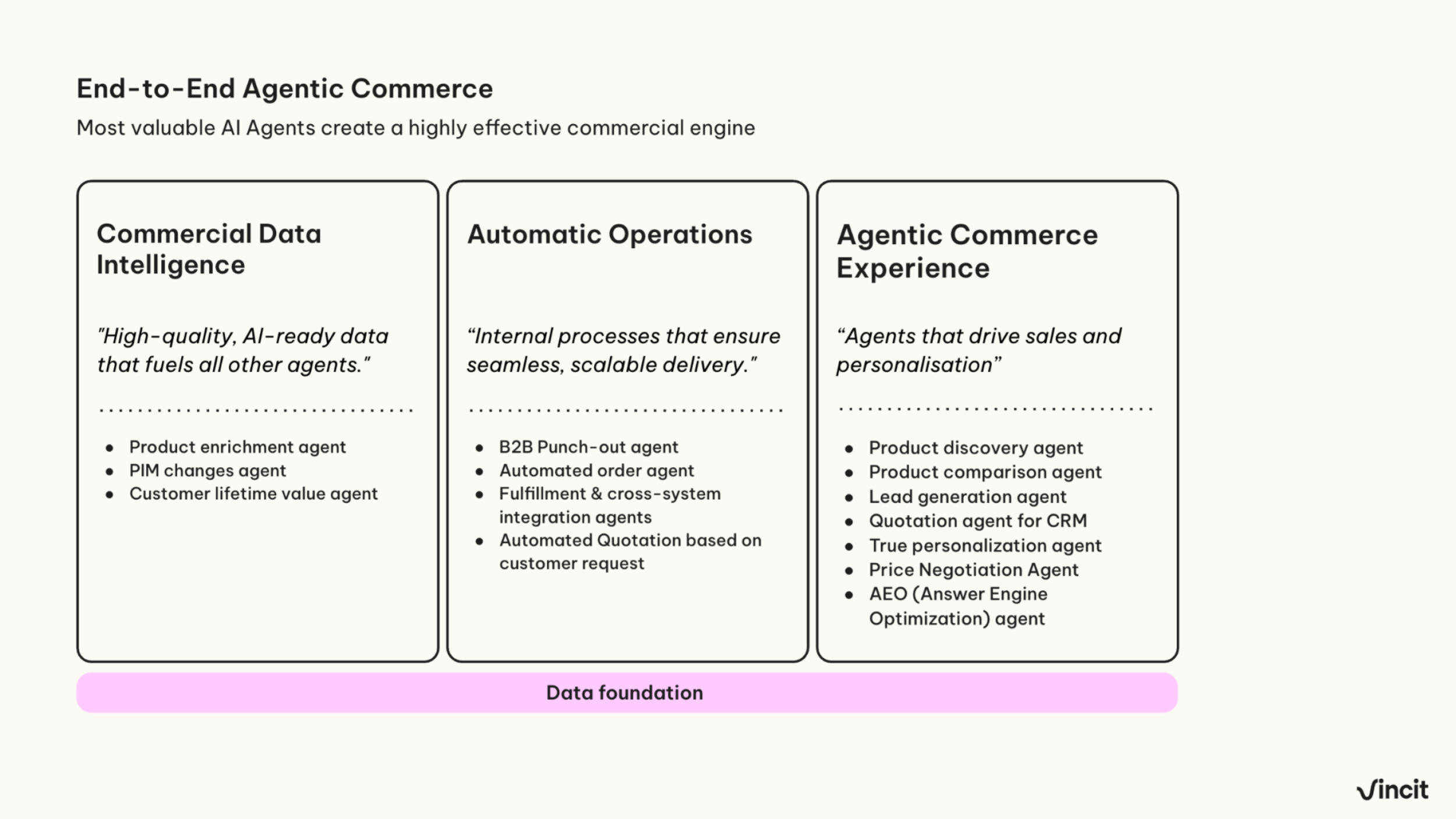
The three areas above include many proven AI agents that deliver real value. This list of agents gives you an idea of what we could be talking about, including the Data Enrichment Agent, Content Agent, Order Fulfillment Agent, Quote Generation Agent, Personalization Agent, Chatbot Agents, and more.
In our use case with the machinery company, the biggest opportunity for the seller goes beyond simply automating sales. It’s about optimizing processes so that people can focus on the bigger picture and drive growth. For any company, the best place to start is by identifying the most important use cases where agentic AI can create real value and impact for business—whether through increased sales or more efficient processes that reduce costs. Naturally, the feasibility of each agentic AI solution is also an important factor when calculating ROI.
Want to discuss how agentic AI could look like for your business? Reach out—we’d be happy to talk.
Riku Kärkkäinen
Commerce Business Area Lead
riku.karkkainen@vincit.fi
Victoria Palacin
Head of Capability and Delivery
Data & AI Business Area
victoria.palacin@vincit.fi

Riku Kärkkäinen,
Business Area Lead, Vincit Commerce


